PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder in women of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is a syndrome, meaning it consists of multiple symptoms and conditions that vary from woman to woman.
A woman with at least two of the following features may be diagnosed with PCOS:
- Excess androgens (“male” hormones) – This can lead to symptoms like excessive facial or body hair (hirsutism), often appearing on the chin or chest.
- Irregular periods – Ovulation does not occur regularly.
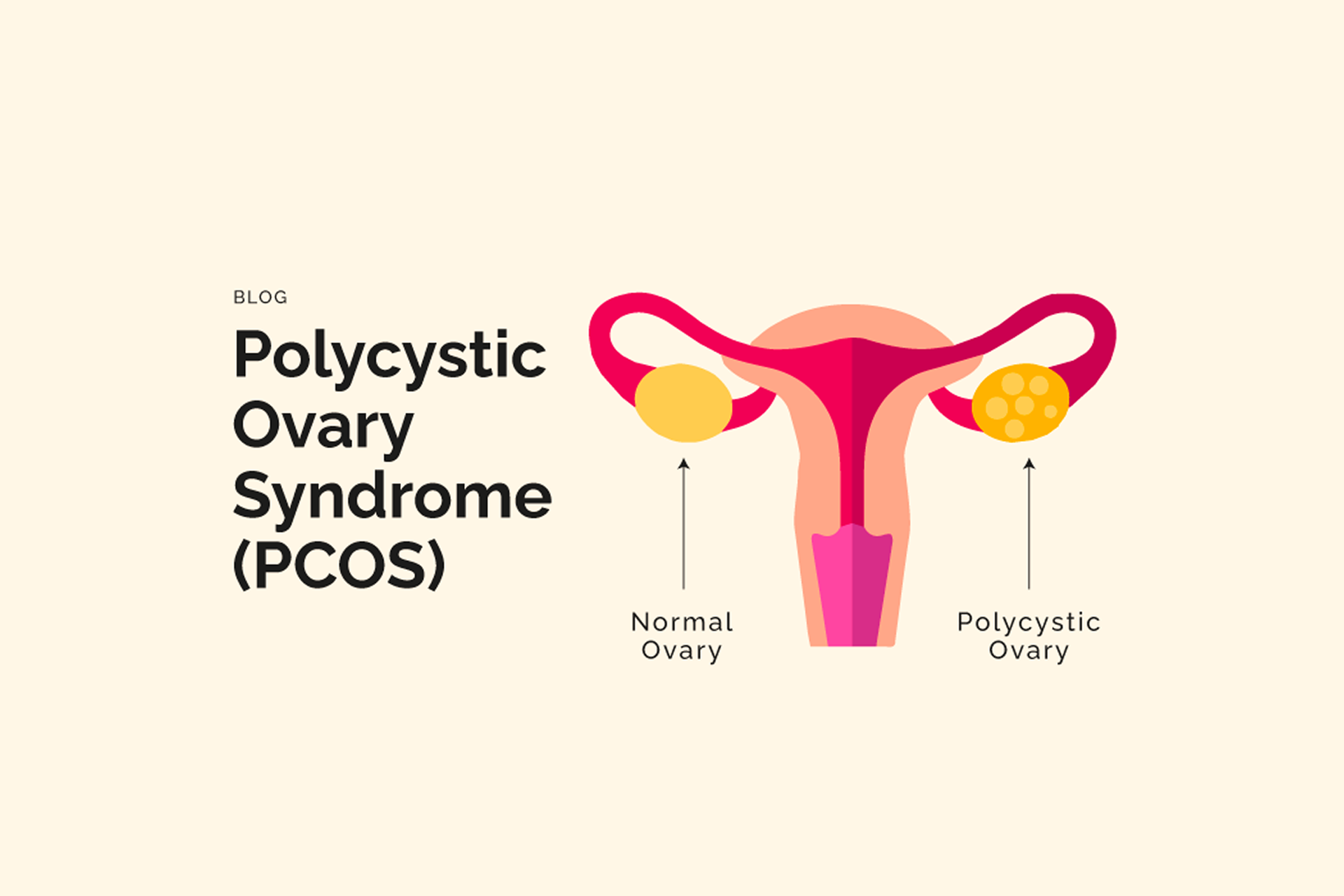
- Enlarged ovaries with multiple follicles – The ovaries contain fluid-filled sacs (follicles) and are larger than normal.
Why is PCOS a Concern?
While some women may not be overly concerned about symptoms like excess hair, the biggest challenge with PCOS is its impact on fertility.
Since PCOS affects ovulation, a woman with this condition has fewer fertility windows, making conception more difficult.
Other common symptoms include:
Weight gain – Often stubborn and linked to insulin resistance.
Hair loss – Similar to male-pattern baldness.
Oily skin & acne – Due to increased androgen levels.
Potential Complications of PCOS
If left unmanaged, PCOS can lead to serious health concerns, including:
Infertility – Due to irregular ovulation.
Abnormal uterine bleeding – Leading to complications like anemia.
Miscarriages – Increased pregnancy risks.
Gestational diabetes & high blood pressure in pregnancy – Affecting both mother and baby.
Metabolic syndrome – A cluster of conditions increasing the risk of heart disease.
Type 2 diabetes – Due to insulin resistance.
Mental health concerns – Higher rates of depression and anxiety.
Endometrial cancer – Due to prolonged exposure to estrogen without ovulation.
The Good News: PCOS is Manageable!
While PCOS cannot be cured, the symptoms can be effectively managed with the right treatment plan.
Diagnosis of PCOS
A medical doctor will diagnose PCOS based on:
Physical symptoms – Including weight distribution, hair growth patterns, and skin conditions.
Medical history & hormone testing – Blood tests to check hormone levels.
Pelvic ultrasound – To assess ovarian size and follicle development.
With proper management, most women with PCOS can successfully conceive and avoid long-term health risks. The key is early diagnosis, lifestyle adjustments, and consistent medical support.
Dr. Tolu Binutu
Treatment Options
The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Hormonal Balance Therapy – Medications to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce excess androgens.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity – Lifestyle changes and medications to enhance insulin response.
Ovulation Support – Fertility treatments for those trying to conceive.
Lifestyle Modifications – Diet and exercise to help control weight and reduce symptoms.
Laser Hair Removal or Medications – For excessive hair growth.
Surgical Options (in severe cases) – Procedures like ovarian drilling to stimulate ovulation.
If you suspect you have PCOS, consult a doctor today to take control of your health!